
Mastering Annual Recurring Revenue: Key Insights and Calculation Tips
- Trendinsaas
- No Comments

Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is a critical metric for subscription-based businesses, offering a comprehensive view of predictable revenue streams. By mastering ARR, companies can better forecast financial outcomes, allocate resources effectively, and identify future growth opportunities. Understanding the calculation and nuances of ARR not only aids in optimizing revenue but also ensures accurate financial planning. With the right strategies, tools, and a focus on customer retention, businesses can leverage ARR to drive long-term success and sustainability in competitive markets.
Introduction to Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)

Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is among the most important KPIs for businesses with subscription-based models. It measures the predictable and steady income a company can expect annually, excluding irregular or one-time payments. ARR provides clarity on a company’s expects financial health and growth potential, making it a key metric for strategic decision-making. With ARR, businesses can create accurate revenue forecasts that help align their goals and resources effectively.
A clear understanding of ARR allows businesses to better manage their financial resources. It simplifies budgeting, enabling companies to allocate funds efficiently across departments such as marketing, operations, and customer success. ARR also serves as a benchmark for tracking performance against competitors and industry standards, making it easier to identify strengths and areas for improvement.
Furthermore, ARR is not just about measuring revenue; it also provides insights into customer behavior. By analyzing ARR trends, businesses can uncover valuable information about customer retention, churn rates, and upselling opportunities to new customers. These insights are instrumental in shaping strategies that promote sustainable growth.
Understanding Recurring Revenue

Recurring revenue refers to income that a subscription model or business earns consistently over time from repeat customers. Unlike one-time sales, recurring revenue offers stability and predictability, making it a cornerstone of subscription-based businesses. This model ensures that a company receives payments at regular intervals, reducing financial volatility and enabling better long-term planning.
For businesses, recurring revenue serves as a reliable foundation for scaling operations. It allows companies to predict cash flow with greater accuracy, ensuring they can meet operational costs and invest in growth opportunities. Moreover, this revenue model fosters stronger relationships with customers, as it emphasizes continuous engagement and value delivery.
Subscription-based businesses benefit significantly from recurring revenue as it helps maintain a consistent income stream. By focusing on customer retention and delivering exceptional value, companies can build a loyal customer base that contributes to sustained revenue growth. As a result, recurring revenue not only ensures financial stability but also creates opportunities for innovation arr growth and expansion.
Calculating Annual Recurring Revenue
The formula for calculating ARR is straightforward yet comprehensive:
ARR = (Total revenue from new subscriptions in a period) + (Recurring revenue from existing subscriptions at the beginning of the period) – (Churned revenue from existing subscriptions during the period) + (Upgrades to annual subscriptions or downgrades to existing subscriptions during the period)
To determine ARR, divide each customer’s total contract value by the duration of their contract in years. Summing up these values gives the total ARR, which reflects the total dollar of revenue generated annually from subscription contracts The formula for calculating ARR is both simple and comprehensive, making it easy for businesses to track their recurring revenue. It is calculated by adding the total revenue from new subscriptions to the recurring revenue from existing customers, subtracting churned revenue, and factoring in any upgrades or downgrades during the period. This detailed approach ensures accuracy and provides a holistic view of a company’s financial health.
When calculating ARR yearly subscriptions, it’s essential to account for the specific terms of customer contracts. For instance, dividing the total contract value by the duration of the agreement provides a clear understanding of how much revenue each customer contributes annually. Summing up these values gives the total ARR, offering a complete picture of annual revenue from subscriptions.
Accurate ARR calculation is critical for making informed financial decisions. It helps businesses identify trends, such as growth rates or potential risks, and adjust their strategies accordingly. By maintaining precision in ARR calculations, companies can ensure that they are making data-driven decisions to support their growth objectives.
ARR vs. MRR: Key Differences
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) and Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) are complementary metrics that provide insights into different aspects of a company’s financial health. ARR is calculated annually, making it ideal for long-term planning and strategic decision-making. On the other hand, MRR provides a more detailed, month-to-month perspective, allowing businesses to track short-term changes.
While ARR offers a macro-level view of a company’s revenue, MRR delivers a granular understanding of financial performance. Businesses often use MRR to monitor their customer acquisition cost, churn, and revenue fluctuations on a monthly basis. This level of detail helps companies identify emerging trends and take corrective actions promptly.
Both metrics are essential for subscription-based businesses, as they serve different purposes. ARR is best suited for evaluating long-term growth potential, while MRR is ideal for tracking operational efficiency. Together, they provide a comprehensive view of financial performance, empowering businesses to make well-informed decisions for existing customers.
Optimizing Your ARR
To optimize ARR, businesses must focus on strategies that enhance customer retention and reduce churn. This involves close collaboration between sales, marketing, and customer success teams to deliver exceptional customer experiences. By addressing customer needs proactively, businesses can foster loyalty and drive long-term revenue growth.
Analyzing customer behavior through cohort analysis can reveal patterns that influence retention and churn. This analysis allows businesses to segment customers based on their behavior and preferences, enabling targeted strategies for each group. Additionally, offering personalized solutions, such as upgrades or add-ons, can further enhance ARR by increasing customer lifetime value.
Investing in customer success initiatives is another effective way to optimize ARR. By ensuring that customers derive maximum value from their subscriptions, businesses can strengthen relationships and encourage renewals. These efforts not only boost ARR but also create a strong foundation for sustainable growth.
Common ARR Calculation Mistakes
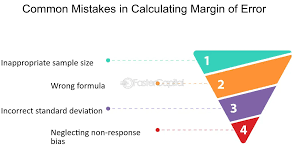
Avoiding mistakes in calculating arr is essential for maintaining accuracy and credibility. One of the most common errors businesses make is failing to account for discounts and price adjustments offered to customers. These discounts, if not factored in correctly, can lead to an inflated ARR, misrepresenting the actual recurring revenue. Similarly, churned revenue—revenue lost from customers who cancel their subscriptions—must be subtracted accurately to ensure ARR reflects the true financial health of the business.
Another common mistake involves including non-recurring revenue sources, such as one-time payments, installation fees, or charges for custom services. While these may contribute to a company’s growth and overall revenue, they are not part of ARR and can distort its calculation. Businesses must strictly focus on recurring revenue streams to maintain precision. Additionally, varying subscription durations among customers can complicate calculations, as companies often overlook adjustments needed to standardize revenue over a one-year period.
To avoid these pitfalls, businesses should implement robust processes for tracking revenue. Automation tools and financial software can ensure that revenue recognition and that discounts, churn, and subscription variations are accounted for accurately. Conducting regular audits of ARR calculations and training financial teams on best practices further minimizes errors, ensuring reliable data for strategic planning.
Using ARR in Financial Planning
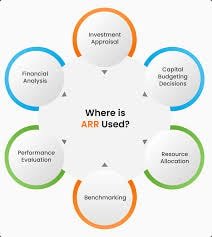
ARR plays a pivotal role in financial planning by providing a clear and consistent forecast of annual revenue. With a predictable forecast revenue stream, businesses can confidently allocate budgets across departments, prioritize investments, and manage cash flow efficiently. This reliability enables companies to focus on long-term growth rather than being distracted by short-term fluctuations in revenue.
Tracking ARR on a year-over-year (YOY) basis allows businesses to monitor their financial trajectory and set realistic growth targets. By analyzing ARR trends, companies can identify areas where they are excelling and where improvements are needed. For instance, a decline in ARR might indicate issues with customer retention or ineffective sales strategies, prompting immediate corrective measures.
Incorporating ARR into financial planning also supports stakeholder confidence. Investors and stakeholders view ARR as a reliable metric for assessing a company’s potential and stability. Regularly reporting ARR in financial statements and presentations demonstrates transparency and builds trust attract investors, further solidifying the company’s position in competitive markets.
Tools and Resources for ARR Calculatio
Modern technology simplifies the process of calculating and tracking ARR, reducing manual errors and saving valuable time. Strategic finance platforms that integrate seamlessly with CRM systems can automate the collection and calculation of revenue data. These tools ensure that ARR reflects the latest subscription changes, including upgrades, downgrades, and churn, without requiring constant manual updates.
CRM software also plays a critical role in managing customer interactions and tracking subscription details. By centralizing data on customer contracts, payment schedules, and subscription durations, these tools help businesses maintain an accurate record of recurring revenue. Additionally, many CRM systems provide built-in analytics features, offering insights into customer behavior and revenue trends.
For companies looking to refine their financial planning further, SaaS valuation templates and recurring subscription revenue management tools can be invaluable. These resources provide standardized frameworks for ARR calculations, enabling businesses to compare their performance against industry benchmarks. Leveraging these tools not only ensures accuracy but also empowers companies to make data-driven decisions for sustained growth.
Best Practices for ARR Management

Managing ARR effectively requires a combination of meticulous attention to detail and strategic foresight. A primary best practice is focusing exclusively on recurring revenue while excluding one-time fees, trial payments, and installation charges. This ensures that ARR calculations accurately represent the business’s long-term financial health.
Regularly reviewing and adjusting pricing strategies is another critical practice. Businesses should analyze market trends and customer feedback to ensure their pricing remains competitive and aligns with customer expectations. Offering flexible subscription plans and add-ons can also enhance ARR by encouraging upgrades and reducing the likelihood of churn.
Clarity and consistency in ARR reporting are vital for effective management. Companies should establish standardized processes for calculating and updating ARR, ensuring that all teams work with accurate and up-to-date information. Frequent cross-department collaboration, particularly between finance, sales, and customer success teams, fosters a unified approach to optimizing ARR and driving growth.
Conclusion
Mastering Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is crucial for subscription-based businesses seeking sustainable growth and stability. By understanding the intricacies of ARR calculations and integrating them into financial planning, companies can ensure accurate revenue forecasting and effective resource allocation. ARR provides businesses with the tools to monitor performance, reduce churn, and enhance customer satisfaction, creating a solid foundation for long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)?
ARR refers to the total predictable and recurring revenue a company can expect annually from its subscription contracts, excluding one-time payments or irregular revenue sources. It is a crucial metric for subscription-based businesses, helping them understand their financial health and long-term growth potential.
2. How do you calculate ARR?
The formula for ARR is:
ARR = (Total revenue from new subscriptions) + (Recurring revenue from existing subscriptions) – (Churned revenue) + (Upgrades and downgrades during the period).
This formula helps businesses assess their recurring revenue streams and forecast future financial outcomes accurately.
3. What is the difference between ARR and MRR?
While ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue) offers a long-term view of a company’s recurring revenue, MRR (Monthly Recurring Revenue) provides more granular insights on a month-to-month basis. ARR is used for long-term financial planning and attracting investors, whereas MRR helps track operational efficiency and customer behavior on a monthly basis.
4. How does ARR help in financial planning?
ARR plays a pivotal role in financial planning by offering a reliable forecast of predictable and recurring revenue. This helps businesses allocate resources efficiently, manage cash flow, and focus on long-term strategies to ensure growth. It also provides key insights into customer acquisition cost, customer retention, and expansion ARR, all of which are vital for sustainable business growth.
5. What are common mistakes in calculating ARR?
Some common mistakes include:
- Failing to subtract revenue lost due to churned customers.
- Including non-recurring revenue like one-time payments.
- Not accounting for varying subscription contract durations correctly.
These errors can distort the true financial picture and hinder revenue recognition accuracy.
6. Why is ARR important for subscription-based businesses?
For subscription-based businesses, ARR is a key metric that reflects the health of the business model. It ensures that a company’s recurring revenue model remains stable, helping attract investors and making future revenue predictions more reliable. ARR provides transparency in financial health, enabling businesses to adjust strategies for optimal growth.
7. What strategies can businesses use to optimize their ARR?
To optimize ARR, businesses should:
- Focus on customer retention and reduce churn.
- Invest in upgrades and add-ons for customers.
- Offer personalized solutions based on customer behavior.
- Align marketing and sales efforts to improve customer acquisition and net customer acquisition rates.
9. What factors influence ARR growth rate?
Factors influencing ARR growth include:
- Successful customer acquisition and retention strategies.
- The adoption of multi-year contracts or annual subscription price models.
- Effective pricing strategies and marketing team performance.
- The introduction of expansion revenue through upselling or cross-selling to existing customers.
10. How do subscription contracts affect ARR?
The terms of subscription contracts play a significant role in ARR calculations. Longer-term contracts with customers provide more stability in forecasting revenue, while frequent contract renewals or upgrades can enhance ARR over time. The contract value and length are integral to calculating the total ARR a company expects to generate.
11. What is a good ARR growth rate for a business?
A good ARR growth rate varies across industries, but a steady increase indicates the company is expanding its customer base, retaining clients, and delivering consistent value. ARR growth is essential for building trust with investors and ensuring that a company’s revenue streams remain stable and scalable.
12. How can businesses improve their ARR calculation accuracy?
To ensure accurate ARR calculation, businesses should:
- Track customer contracts diligently, including renewals, upgrades, and cancellations.
- Use financial tools and software to automate and standardize the ARR calculation process.
- Regularly audit and reconcile revenue recognition practices to eliminate errors.
13. How does ARR help in evaluating operational efficiency?
By analyzing ARR trends, businesses can evaluate their operational efficiency. A healthy growth rate in ARR reflects effective customer acquisition, retention, and resource allocation. Conversely, stagnating ARR could indicate inefficiencies in operations or marketing strategies that need to be addressed.
14. Can ARR be applied to SaaS businesses?
Yes, ARR is particularly valuable for SaaS businesses, where subscriptions form the core of the revenue model. ARR helps SaaS companies maintain predictable and recurring revenue, monitor customer behavior, and plan for long-term scalability and growth.
15. What is the role of pricing strategy in ARR optimization?
A well-defined pricing strategy is essential for optimizing ARR. Businesses must align their subscription pricing with market expectations and customer value. Flexible plans, discounts, and annual contract options can help increase customer lifetime value and boost ARR over time.
